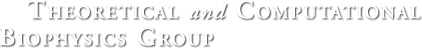Highlights of our Work
2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001
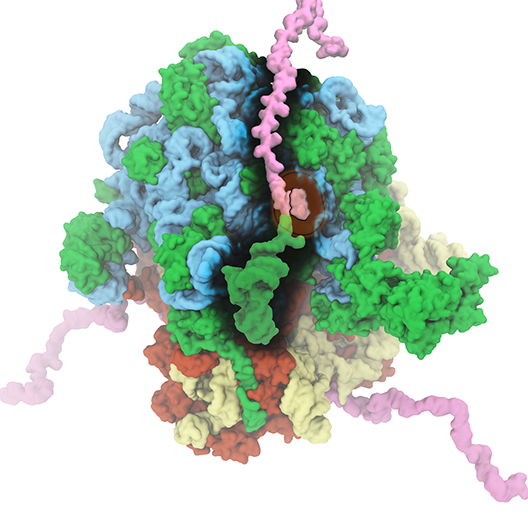
image size:
816.0KB
made with VMD
The ribosome is the ubiquitous machine in all living cells responsible for
translating the cell's genes into functional proteins.
The majority of antibiotic drugs target the ribosomes of bacterial cells while
leaving human ribosomes unharmed.
An example are the most widely-prescribed antibiotics, erythromycin and telithromycin.
They kill bacteria by changing the properties of bacterial ribosomes and, thereby,
disturb the bacterial protein production (see the Oct 2014 highlight Antibiotic Action on the Ribosome).
However, modern bacteria fight antibiotic drugs;
exposing them to a specific kind of antibiotic drug for too long will
trigger the expression of drug-resistance genes, which protect the bacteria,
eventually making the drug useless.
Due to historical overuse of antibiotic drugs,
clinic antibiotic drugs have experienced today serious drug-resistance problems.
In a joint effort of computational and biomedical investigations, reported recently,
molecular dynamics simulations with NAMD and systematic mutation experiments showed that
the above antibiotics interact in a bacterial ribosome with a drug resistance
gene - coded nascent protein and make it stall translation; however, engineered
simple mutations in the bacterial gene can abolish stalling and, thereby,
prevent the effect of drug resistance genes.
The research suggests that engineered mutations might be a strategy to prevent
antibiotic resistance.
Read more on our Ribosome website.
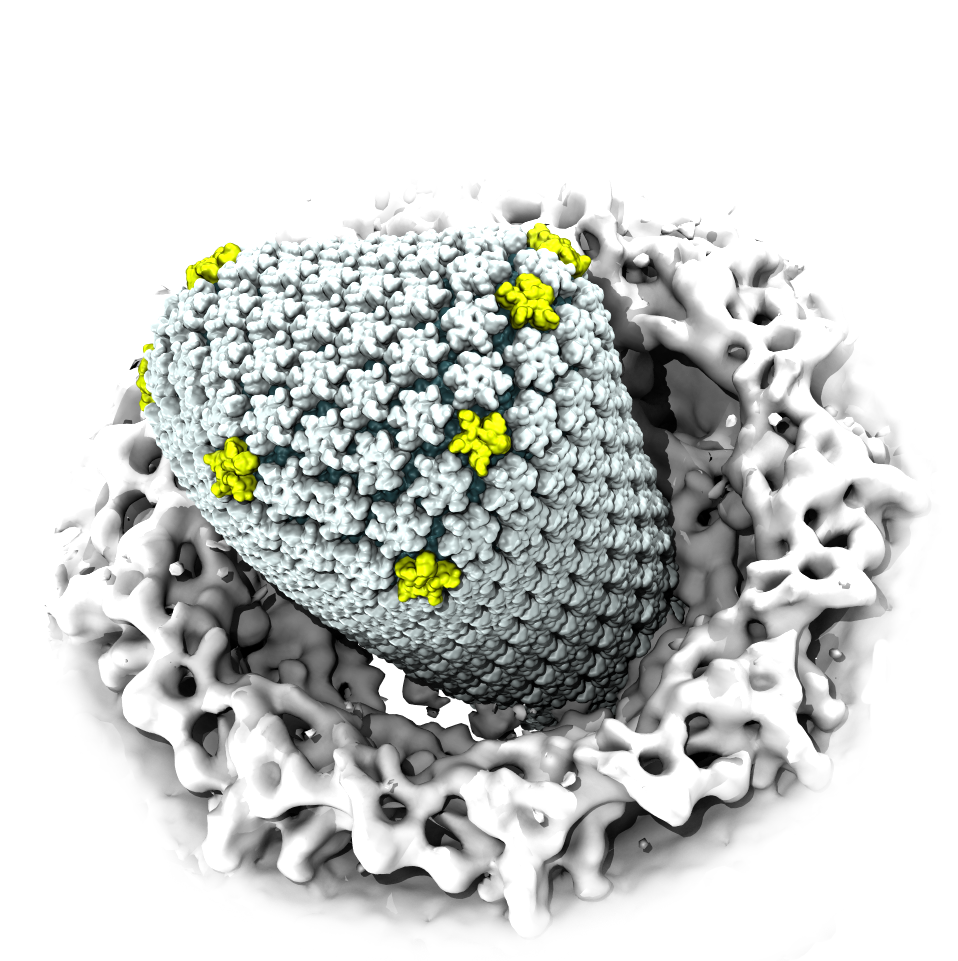
image size:
283.9KB
made with VMD
When human immundeficiency virus (HIV) infects a human cell, it
releases into the interior of the cell its capsid (made of about 1,300
identical so-called CA proteins), a closed, stable container that
protects the viral genetic material (see also June 2013 highlight Elusive
HIV-1 Capsid and August 2015 highlight Anatomy
of a Dormant Killer). Once in the cell ― while avoiding
detection by cellular proteins ― the capsid deceives the cell and
directs the cell machinery to transport it to the nucleus. The
human-cell protein Cyclophilin A (CypA) is thereby exploited to act
against the cell's well being and to assist the HIV infection by
getting the capsid to access the cell nucleus; this results in a
delicate choreography accomplished by escaping anti-viral proteins in
the cell and deceiving transport proteins at the nucleus, all of which
contain a CypA domain that interacts directly with the capsid. Despite
the availability of the crystal structure of the complex of CypA and
CA proteins determined nearly 20 years ago, the mechanism by which
CypA assists the capsid has been unclear due to the lack of
information on CypA in complex with not one CA protein, but the entire
capsid. In collaboration with experimental groups,
computational biologist have shown in a recent report that
the effects of CypA on the capsid are not only structural, but also
dynamical. Thus, new therapeutic strategies may be envisioned through
modulation of the dynamics of the capsid by small-molecule (drug) compounds
that inhibit the binding of CypA to the capsid. More information is
available on our retrovirus website and in
a YouTube video.
The Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group (TCBG), funded by National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation, is not only the developer of the widely used computational biophysics programs
NAMD and
VMD,
but is also an ardent teacher and trainer in computational biophysics. The group has just completed its 40th hands-on computational biophysics training workshop
(see complete list),
having now taught over 1,200 participants in intense, face-to-face, practical training sessions in small groups, typically of 30 students. Participants are faculty, postdocs, industry professionals, and graduate students. The training material, in the form of very extensive tutorials, is freely available on the TCBG
tutorial website.
The workshops are continuously improved, based on participant feedback and on the evolution of NAMD and VMD. TCBG intends to continue the workshops, and is presently developing a new generation of training features built directly into NAMD and VMD in the form of the new user interface qwikMD. For more information, see the
TCBG training website.
Through crystallography researchers have solved the structures of many molecules, chemists those of small organic and inorganic molecules produced via chemical synthesis and biologists those of large macromolecules as they arise in living cells. But the borderline between small and large is not well defined and indeed chemical
synthesis produces today supramolecules, namely, coordination cages, abiological foldamers, metal-organic frameworks and covalent-organic frameworks, that are of similar size and disorder as biological macromolecules, yet, elicit extremely intricate electronic properties resembling the small-molecules. To image the supramolecules
chemists and biologists have now joined forces as reported recently . Key to their strategy are methods developed earlier by computational structural biologists, xMDFF (see August 2014 highlight xMDFF Enhances X-Ray Structures) and PHENIX , and by biomolecular modelers, NAMD (see Jan 2015 highlight NAMD 2.10 Advances Simulations Large and Small ) and ffTK (see Sep 2013 highlight May the Force be With You ), that were imported to chemistry. The team focussed on the structural description of the molecule cyanostar, an anion-sensing organic macrocycle. Two cyanostar molecules forming a pair were resolved atom-by-atom in two distinct stereoisomeric forms, at an extremely high resolution of 0.84 Å, with flexible solvent molecules sitting in their macrocyclic and intermolecular void spaces.
More on our
MDFF website.
A major activity in living cells is the manufacture of new proteins. For this
purpose cells utilize hundreds of ribosomes that read genetic material and
according to the genetic sequence synthesize new protein (See also
Managing the Protein Assembly Line, Born
to Control,
Shutting Down
the Protein Factory).
This crucial synthesis is highly controlled, in particular, in regard to
avoidance of errors. For example, proteins of all living systems are made
solely of so-called L-amino acids and not the closely related D-amino acids, L-
and D-amnio acids being related like left and right hand. Life could have
emerged from either "left-handed" or "right-handed" amino acids, but in living
cells on Earth, protein synthesis occurs exclusively with L-amino acids, despite
of the fact that D-amino acids are actually abundant in organisms and there are
neither geometric nor energetic reasons preventing D-amino acid incorporation.
For example, D-Serine in the human central nervous systems are present at very
high concentrations in vivo. So, the ribosome must have developed early on
in evolution mechanisms that prevent incorporation of D-amino acids into nascent
proteins. In a recent report,
experimental and computational biologists reported
their discovery how the ribosome readily discriminates between L- and D-amino
acids within its catalytic center. Read more on our
Ribosome website.
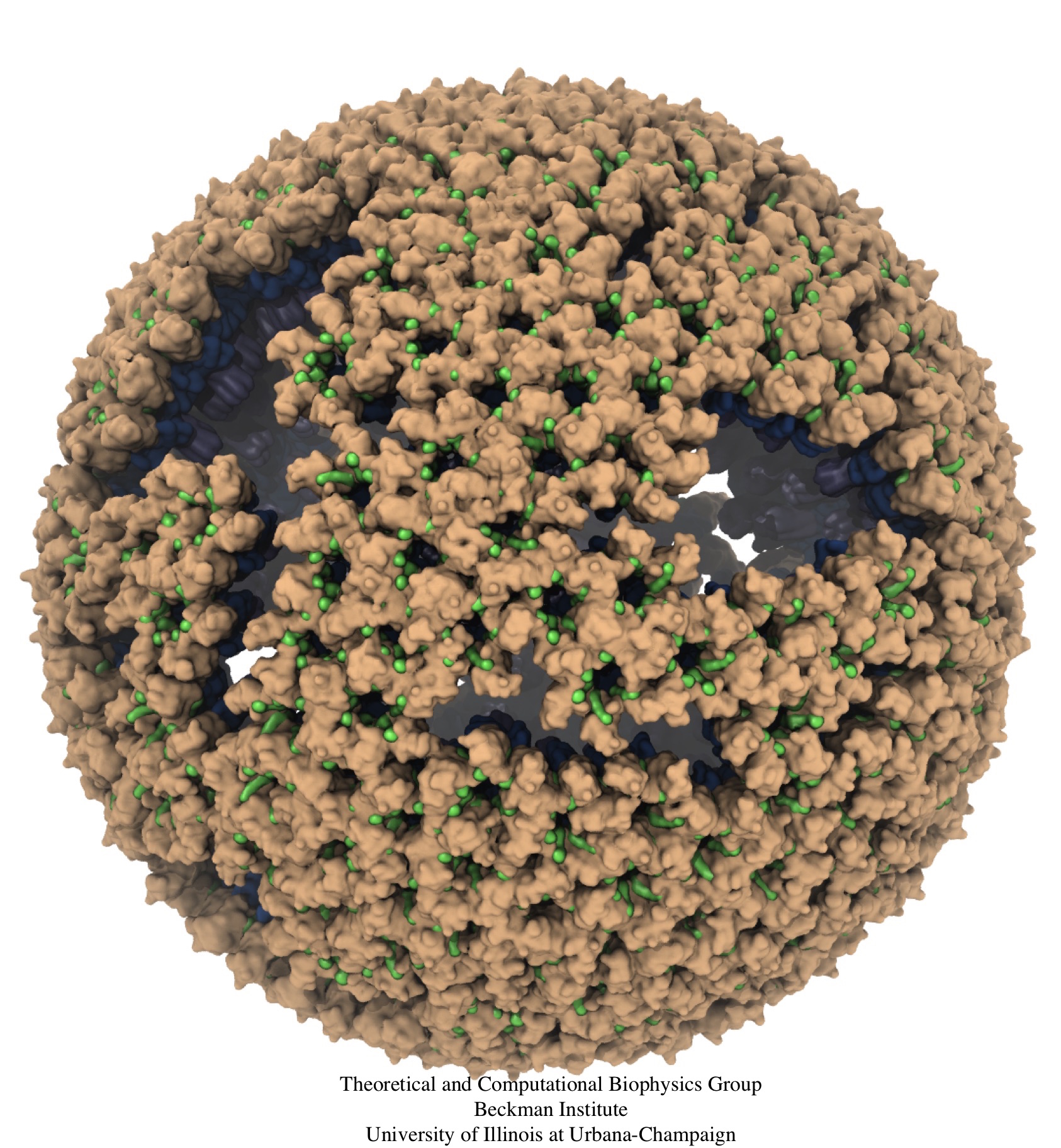
image size:
2.6MB
made with VMD
Retroviruses are parasites that pose a major health threat to humans
(for example in case of HIV) and other animals (for example in case of
RSV, M-PMV, MLV, and many more viruses).
After a retrovirus hijacks a cell, the infected cell produces
multiple copies of the virus which are then released into
the host's bloodstream.
These newly released viruses must mature before they can
infect other cells. A strategy for preventing virus spread is therefore,
to lock the viral particles in their immature, non-infectious state.
However, to render the immature virus an attractive target for
structure-based drug development one needs to know its chemical structure.
Unfortunately, the complexity and size of the viral particle ―
an incomplete hexagonal shell with a size close to 100 nm ―
have prevented the experimental determination of the chemical, namely atomic level,
structure of the virus.
As reported recently,
a team of computational and experimental researchers have provided an atomic
structure of the immature retroviral lattice for the Rous Sarcoma
Virus. The multi-domain RSV model was derived through a combination of
state-of-the-art modeling techniques, including, cryo-EM-guided
homology modeling, large-scale molecular dynamics simulations
using enhanced sampling capabilities available in NAMD,
together with experimental measurements such as X-ray
crystallography and a wealth of biochemical data.
Particularly, the model reveals novel
features of the packing and dynamics of the immature capsid protein
with implications for the maturation process and confirms the
stabilizing roles of the so-called upstream and downstream domains
of the immature RSV. More information is available on
our retrovirus website, and in
a highlight video.
image size:
901.7KB
made with VMD
Synthesis and placement of new proteins in a living cell poses a challenge for the cellular machinery, in particular in case of so-called membrane proteins. Starting with nothing more than a sequence of DNA, the cell has to translate the genetic code, stitch together the constituent amino acids, and then place the newly made protein where its function is needed, namely the cell membrane. To meet the challenge the cell employs a molecular machine for the synthesis of proteins, the ribosome (see the Dec. 2009 highlight on Managing the Protein Assembly Line ), as well as special proteins that translocate newly synthesized proteins out of the machine into the cell membrane (see the Feb. 2011 highlight on Placing New Proteins ). Depending on the complexity of the membrane protein insertion, different protein systems are used for the translocation, in most cases the systems involving complexes of several, even many, proteins. Now however, the structure and function of the simplest translocating protein system has been solved, which actually is made of only a single protein, called YidC. Despite its simplicity, structure determination of YidC was difficult, taking three decades. Successful structure determination was recently reported here, and involved the combination of cryo-electron microscopy, mutational experiments and computer simulations, the latter using NAMD, VMD and MDFF. The structure that was discovered shows a distinctive arrangement of five trans-membrane helices and reveals how a single copy of YidC interacts with the ribosome at the ribosomal tunnel exit and identifies a site for membrane protein insertion at the YidC protein-membrane lipid interface.
The quality of this atomic model is validated by its close agreement with a recently published crystal structure of E. Coli YidC (here).
More on our protein translocation website.
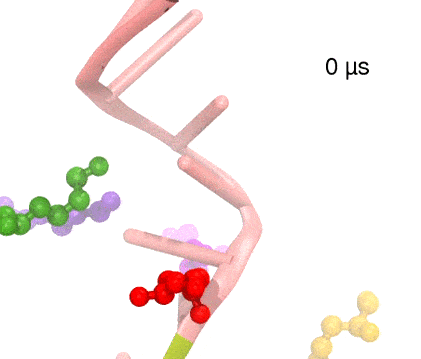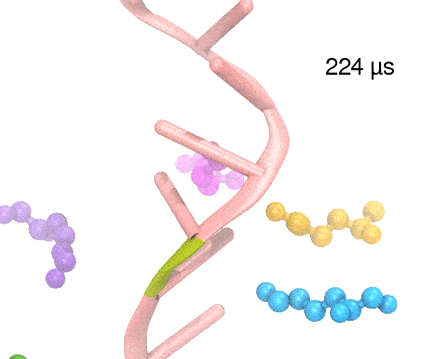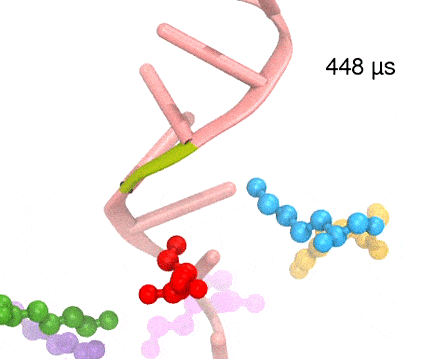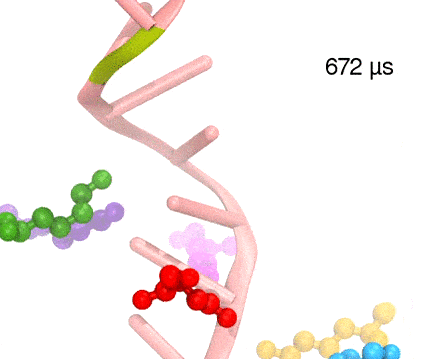
image size:
680.4KB
made with VMD
Many processes in living cells require molecular motors. Examples are transport of cargo within a cell, degrading misfolded proteins, and controlling gene expression. In the latter case acts a motor, called Rho, that moves along messenger RNA. The energy of the cell's motors stems from molecules of ATP that are converted to ADP, release thereby energy and drive motor action. How exactly this happens remained largely a mystery, despite decades of study and despite the availability of detailed molecular structures of the motors. A molecular dynamics study employing NAMD has achieved a great breakthrough in resolving the mechanism by which ATP-to-ADP conversion drives Rho to translocate along RNA. While molecular dynamics simulation, in principle, is well suited to explain Rho's motor action, the problem was that the action takes about a millisecond which is a time period beyond such simulations' reach. Employing new sampling methods, a recent publication, reported in new, complete and fascinating detail how Rho works. The simulations permitted literally to look under the hood of Rho's engine and see how it pulls itself along RNA and coordinates a cyclic and repeated motor action. It turned out that Rho, a ring of six identical protein subunits, engages in an ATP-to-ADP conversion-induced periodic motion of the subunits that pushes RNA electrostatically through the ring center. A completely surprising finding was the existence of coordination switches that make each ATP-to-ADP conversion lead to exactly one forward step along the RNA and keep the six subunits strictly synchronized, turning a randomly moving protein system into a well-behaved engine. More on our molecular motor website.
Long-range electrostatic interactions control macromolecular processes
within living cells as prominent charges appear everywhere,
such as in DNA or RNA,
in membrane lipid head groups, and in ion channels. Reliable and
efficient description of electrostatic interactions is crucial in
molecular dynamics simulations of such processes. Recently a new
mathematical approach for calculating electrostatic interactions, known as
multilevel summation method (MSM),
has been developed and
programmed into
NAMD 2.10
as reported
here.
Compared to the earlier decades-long approach,
the particle-mesh Ewald (PME) method, MSM provides more flexibility
as it permits non-periodic simulations like ones
with asymmetric charge distributions
across a membrane
or of a water droplet with a protein folding inside. Furthermore,
MSM is ideally suited for modern parallel computers, running,
for example, simulations
of large virus particles. More information
here.
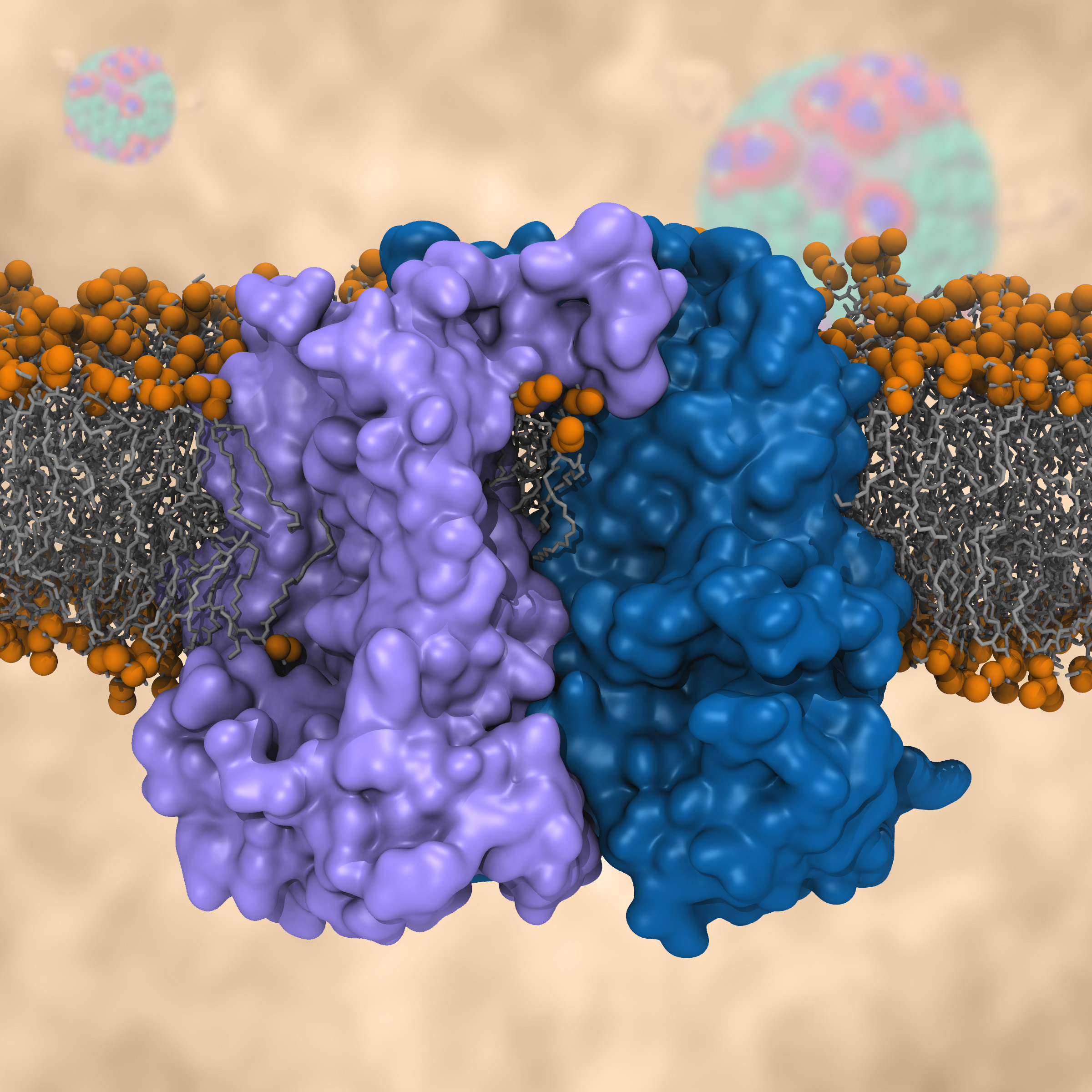
image size:
1.3MB
made with VMD
Most living cells acquire their energy through photosynthesis or respiration, both of which convert input energy (sun light or food, respectively) through coupled electron and proton transfer processes. A key role is played here by a protein, called the bc1 complex, that intermediately stores energy through the reaction of molecules of quinol into molecules of quinones, utilizing energy released to pump protons across an intracellular membrane. This reaction is initiated in the bc1 complex at the site of binding of the quinol molecule, but critical details about the physical mechanism leading to coupled electron-proton transfer are still unknown. A recent study, based on molecular modeling with NAMD and quantum chemistry calculations, investigated possible reaction mechanisms in case of the bc1 complex from the bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus. The calculations suggest a novel configuration of amino acid residues responsible for quinol binding in the bc1 complex, and support a mechanism for coupled proton-electron transfer from quinol to iron-sulfur cluster. The study opens the door for a complete simulation description of the crucial role of the bc1 complex in bioenergetics. More about the bc1 complex can be found here.
VMD ..." />
The 1.9.2 release of VMD promises more insight and more beauty from use of
an already powerful molecular visualization and analysis program.
For more insight, VMD 1.9.2 exploits the power of parallel
computers small and large to reduce analysis runtimes tremendously,
as
reported here,
and
here.
VMD 1.9.2 strengthens collaboration between experimental and computational
biologists in resolving atom-by-atom structure and dynamics of huge
molecular assemblies arising in living cells by guiding interactively a
match of computational model to experimental data, as
reported here;
this is achieved through quality-of-fit cross correlation to be
computed rapidly using GPUs, the fastest means of modern calculation.
Many new and updated tools, called plugins, developed by the VMD user
community, are included in VMD 1.9.2, including
force field parameterization,
helix analysis,
and normal mode plugins.
VMD 1.9.2 incorporates a new
remote control
and works with Android phones and tablets.
For more beauty, VMD 1.9.2 adds stunning interactive graphics on
laptops. Such high quality graphics was previously available only on the
most advanced computers, through powerful GPU-accelerated interactive ray
tracing. Interactive ray tracing makes the task of getting a molecular
image "just right" much easier than ever before; it also enables
rendering of spectacular movies, turning scientists into great film
directors. More details about VMD 1.9.2 features can be found
here.
See the light harvesting movie produced with VMD 1.9.2 here.
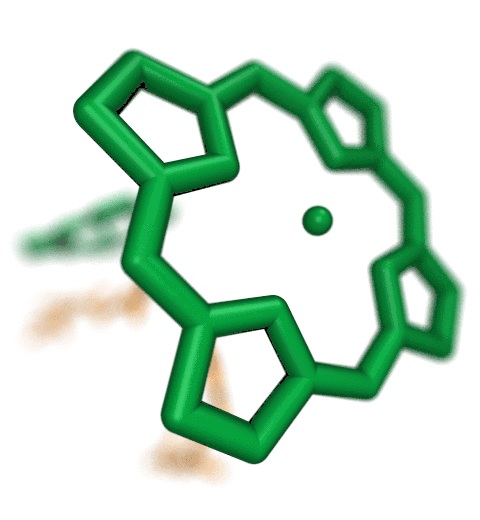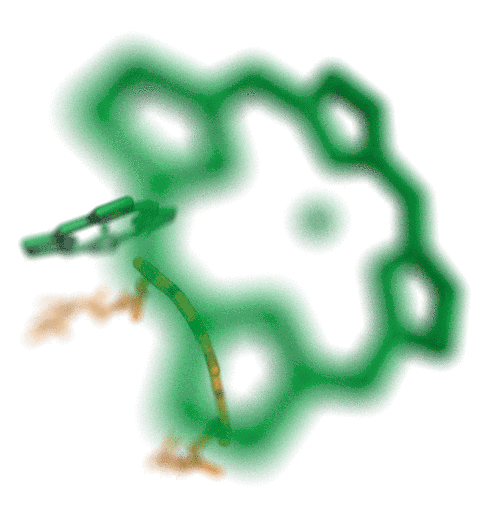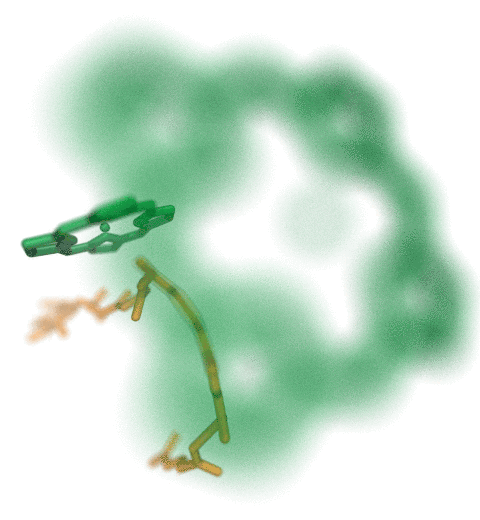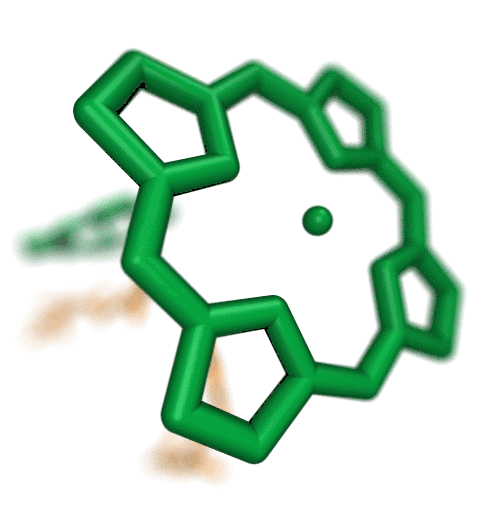
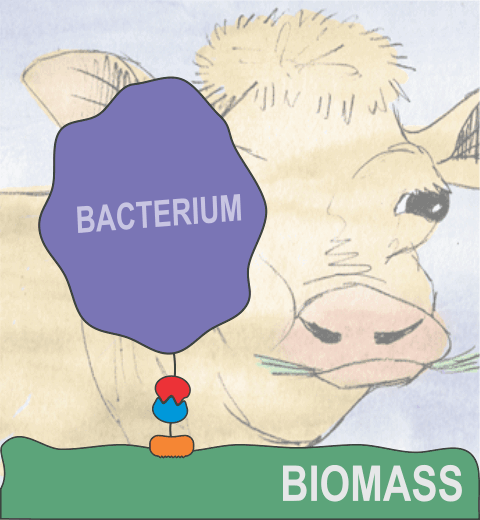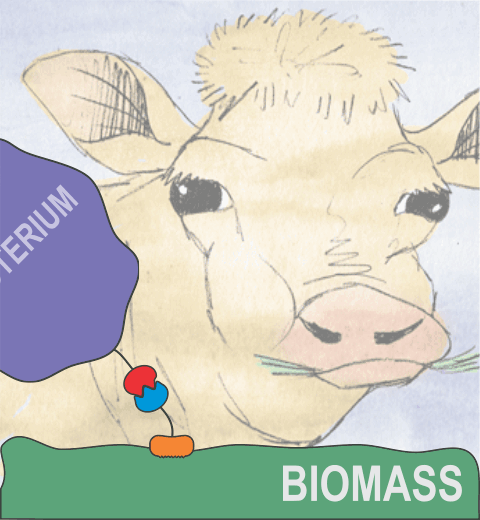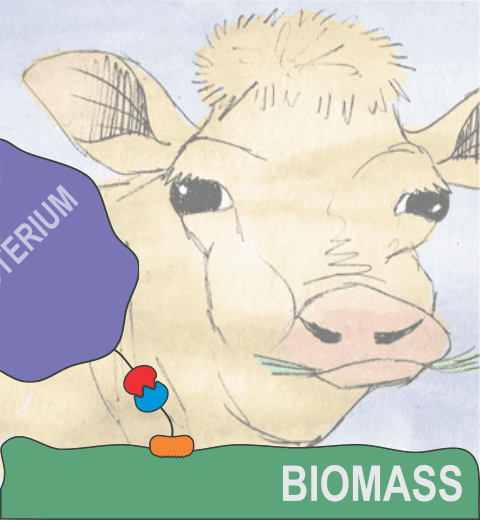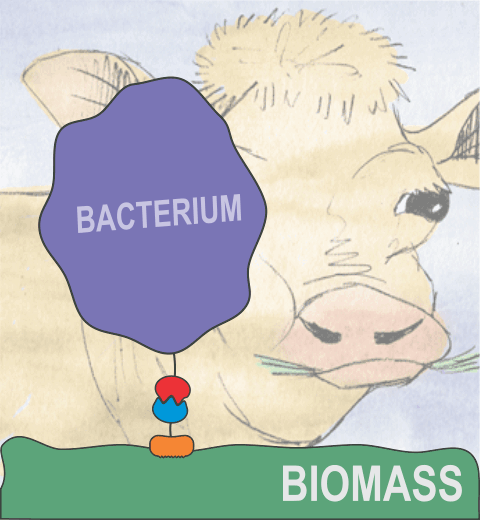
Bacteria can make a living from a very wide range of food sources. This ability makes them, for example, essential symbionts in animal digestive tracts where they assist their hosts in breaking cellulose fibers up into compounds degradable by the animal metabolism. Today, human gut bacteria, part of the human microbiome, are one of the hottest research topics in medicine. Gut bacteria face a particularly tough job in the rumen of the cow where they digest hardy cellulose fibers of grasses. Key to the job, taking place in a constantly moving fluid, are molecular tentacles, so-called cellulosomes, on the surface of the symbiotic bacteria. The cellulosomes develop a tight grasp on and then effective cleavage of cellulose. In a joint experimental-computational study researchers have investigated how in case of the bacterium Ruminococcus flavefaciens cellulosomes are built in a modular way, with molecular modules easily binding and unbinding during cellulosome construction, but sticking extremely strongly together during cellulosome digestive activity. As reported recently, single molecule force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations using NAMD could show that under strain the adhesive bonds between cellulosome modules become stronger than seen in any other biomolecular system, in fact, become nearly as tight as strong chemical bonds. While the experimental data revealed bond strength and other characteristics, simulations reproducing the observed data provided a detailed view of the adhesive bond at atomic resolution, thereby revealing the physical mechanism underlying the uniquely adhesive property of cellulosomes.
Gut bacteria and cellulosomes can be employed in 2nd generation biofuel generation (see highlight Waste into Fuel). More on gut bacteria and cellulosomes on our biofuels website.
NAMD
includes numerous enhancements to ..." />
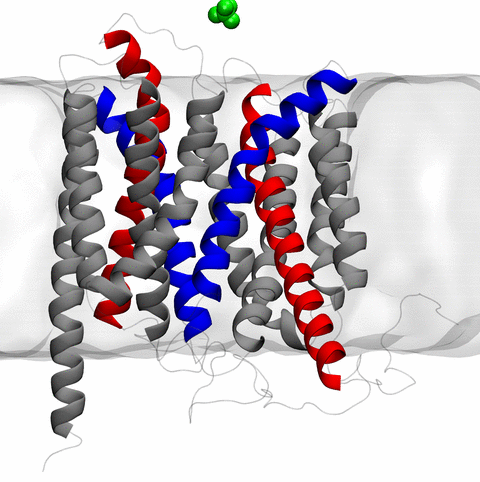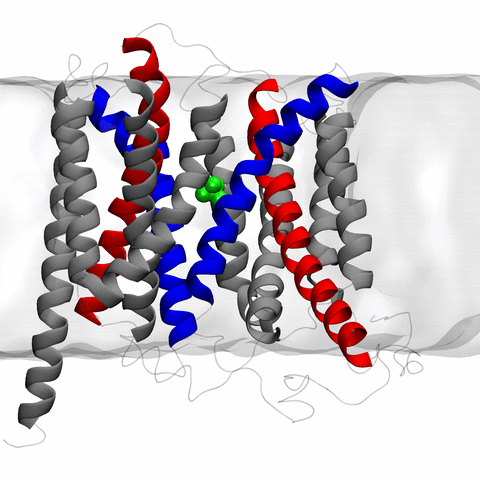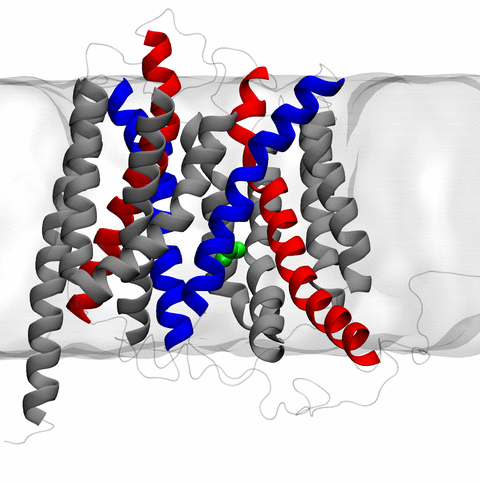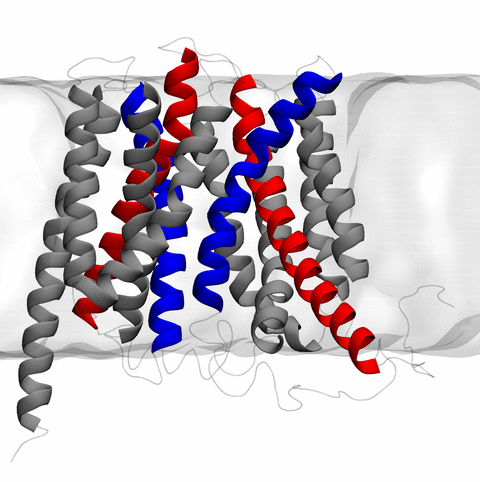

image size:
11.9MB
made with VMD
The 2.10 release of
the molecular dynamics program NAMD
includes numerous enhancements to support simulations
of massive supramolecular assemblies such as the HIV capsid (see highlight
Elusive HIV-1 Capsid).
A single such simulation of a hundred million atoms or more can
utilize the tens of thousands of processors of petascale supercomputers
thanks to recent advances in computational methodology
reported here.
Equally if not more significant, however, are advances in NAMD's
implementation of multiple copy algorithms for enhanced sampling of
smaller molecular systems as
reported here.
These algorithms have already allowed
researchers studying the molecular machinery of living cells
to reveal for the first time with NAMD
mechanisms operating on timescales of milliseconds or longer,
including
the rotary action of the ubiquitous energy conversion complex ATP synthase
and the inward to outward opening transition of
the membrane transporter protein GlpT, shown in the accompanying animation.
NAMD 2.10 also introduces multilevel summation,
reported here,
a major algorithmic advance
enabling efficient long-range electrostatics for non-periodic and semi-periodic simulations.
More on new features in the 2.10 release of NAMD can be found
here.