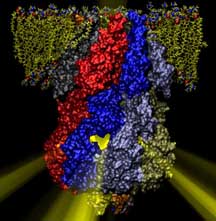
Release 3.0 of NAMD retains the same well-known parallel scaling
capabilities of previous versions while adding improved support
for GPU acceleration. A new GPU-resident mode has been introduced
that more than doubles simulation performance for a single GPU and
scales more efficiently across NVIDIA DGX architectures than NAMD's
GPU-offload mode provided in the earlier version 2.x releases.
With GPU-resident mode,
NAMD
is capable of simulating small systems,
such as the 24k-atom DHFR using AMBER force field parameters, at a
rate of more than
1 microsecond of simulated time per day.
Several
advanced features and enhanced sampling methodologies
are available for GPU-resident mode,
such as alchemical free energy methods,
the Colvars collective variables module, and TCL forces.
The Future of Biomolecular Modeling
A 2015 TCBG Symposium brought together scientists from across the Midwest to brainstorm about what's on the horizon for computational modeling. See a summary of what these experts foresee.
Read more
Computational Biology of Membrane Proteins
Since 1988 Illinois researchers have consistently honed their skills in parallel computing, which enabled them to elucidate dynamic processes occurring in many membrane proteins and produce exciting discoveries. By Lisa Pollack
Read more
Announcements
Electron transport through peptidesTCBG members on TV newsSparing healthy microbes while using a novel antibioticTajkhorshid receives Beckman Institute Vision and Spirit Award
Seminars
Remembering Klaus Schulten
Recent Publications All Publications
- GOLEM: Automated and Robust Cryo-EM-Guided Ligand Docking with Explicit Water Molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2024.
- Broadening access to small-molecule parameterization with the force field toolkit. J. Chem. Phys., 160:242501. 2024.
- Topological Learning Approach to Characterizing Biological Membranes. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 64:5242-5252. 2024.
- APACE: AlphaFold2 and advanced computing as a service for accelerated discovery in biophysics. PNAS, 121:e2311888121. 2024.
- Improved Highly Mobile Membrane Mimetic Model for Investigating Protein–Cholesterol Interactions. Nat. Commun., 64:4822-4834. 2024.
- A Gram-negative-selective antibiotic that spares the gut microbiome. Nat. Commun., 630:429-436. 2024.
- Beyond nothingness in the formation and functional relevance of voids in polymer films. Nat. Commun., 15:2852. 2024.
Highly Cited
Steered molecular dynamics simulations of force-induced protein domain unfolding. PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Genetics, 35:453-463, 1999.
Click here for other highly cited papers
Click here for other highly cited papers