TCBG Software at SC08

|
SC08 Talks and Demonstrations
|
Conference Paper Presentation
Graphics processing units (GPUs) have become an attractive option for accelerating scientific computations as a result of advances in the performance and flexibility of GPU hardware, and due to the availability of GPU software development tools targeting general purpose and scientific computation. However, effective use of GPUs in clusters presents a number of application development and system integration challenges. We describe strategies for the decomposition and scheduling of computation among CPU cores and GPUs, and techniques for overlapping communication and CPU computation with GPU kernel execution. We report the adaptation of these techniques to NAMD, a widely-used parallel molecular dynamics simulation package, and present performance results for a 64-core 64-GPU cluster.
Conference Tutorial Presentations
NVIDIA's CUDA is a general purpose scalable parallel programming model for writing highly parallel applications. It provides several key abstractions--a hierarchy of thread blocks, shared memory, and barrier synchronization. This model has proven quite successful at programming multithreaded manycore GPUs and scales transparently to hundreds of cores: scientists throughout industry and academia are already using CUDA to achieve dramatic speedups on production and research codes. A new compiler backend extends CUDA to multicore CPUs. In this tutorial NVIDIA engineers will partner with academic and industrial researchers to present CUDA and discuss its advanced use for science and engineering domains. The morning session will introduce CUDA programming and the execution and memory models, motivate the use of CUDA with many brief examples from different HPC domains. The afternoon will discuss advanced issues and include real-world case studies from domain scientists using CUDA for computational biology, computational fluid dynamics and seismic imaging.
NIH National Center for Research Resources Booth Exhibit
The NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics and Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group is located at the Beckman Institute of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The Resource brings advanced molecular modeling, bioinformatics, and computational technologies to bear on questions of biomedical relevance through direct collaboration with experimental researchers, the distribution of user-friendly cutting-edge software, and a broad range of training and dissemination activities.
The flagship software packages NAMD and VMD, both distributed free of charge with source code, facilitate the discovery process from analysis, through modeling, to visualization of the molecular apparatus in biological cells:
- NAMD, recipient of a 2002 Gordon Bell Award, is a parallel molecular dynamics code used regularly to simulate systems of 1,000,000 atoms and beyond on both large supercomputers and inexpensive Linux clusters.
- VMD is a molecular visualization program for displaying, animating, and analyzing large biomolecular systems using hardware-accelerated 3-D graphics and built-in scripting.
Both packages have been adapted for GPU acceleration using the CUDA programming system from NVIDIA. This work is described at SC08 in tutorial M02, "High Performance Computing with CUDA" (all day Monday), and technical paper 323, "Adapting a Message-Driven Parallel Application to GPU-Accelerated Clusters" (Tuesday, 11:30pm-12pm, Ballroom E). Demos may be viewed at the NVIDIA and Sun booths.
NVIDIA and Sun Booth Demo
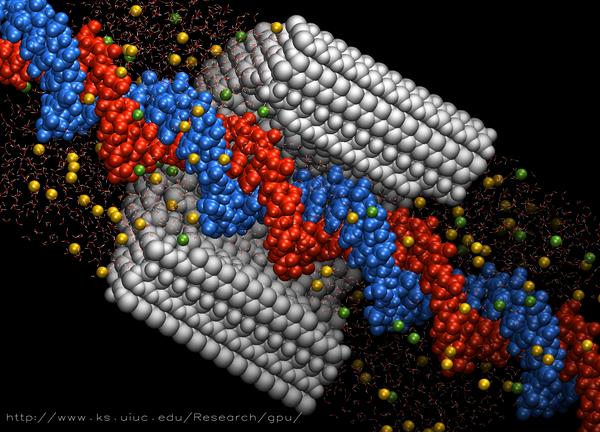
Live CUDA-accelerated simulation of DNA passing through a synthetic nanopore. Information on the science of this simulation is available at http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/nanopore/, and on GPU acceleration at http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/gpu/.